If you own a Shopify store that is based in one of the countries of the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council), it is important that you learn how to charge taxes correctly to your customers with respect to the new tax rules in this region.
On January 1, 2018, VAT (Value Added Tax) was introduced in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia (KSA) with more GCC countries to follow in the near future.
Your obligation to charge taxes on your online sales is dependent on whether your business (the company that runs your store) is VAT-registered or not.
You are required to register for VAT within 30 days if you are a GCC based business selling goods or services in the UAE or KSA and either:
- Your turnover was more than AED/SAR 375,000 in the last 12 months; or
- You expect that your yearly turnover will exceed AED/SAR 375,000.
You can voluntarily register for VAT if you are a GCC based business selling goods or services in the UAE or KSA and your turnover or expenses (which will be subject to VAT) were more than AED/SAR 187,500 in the last 12 months.
Each VAT registered business is assigned a TRN (tax registration number) or TIN (tax identification number) from the tax authority.
A standard VAT rate in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia is 5%. This rate is uniform across all emirates such as Dubai or Abu Dhabi.
If your annual turnover is below the VAT registration threshold, that is if your business is not VAT registered, you do not charge VAT on your sales regardless of where your customers come from.
If your business is VAT registered, you have to charge VAT to some customers. You also need to include your TRN on your invoices and receipts in order for them to be valid.
There are two factors that affect whether you should or should not charge taxes — what country the customer is from and whether they are a consumer (B2C) or a business (B2B).
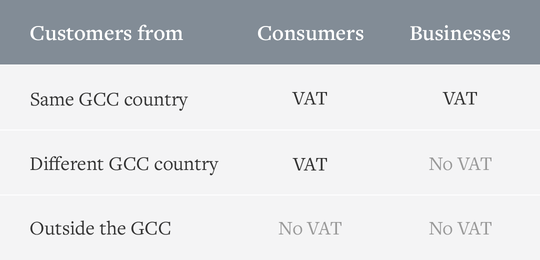
When selling to consumers and businesses in your home country, you should always charge VAT and use the VAT rate of your country. This applies to selling both physical and digital goods.
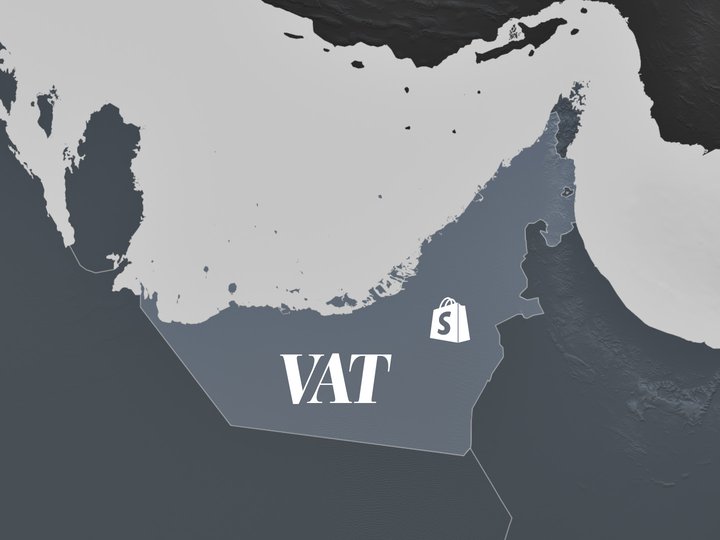
When selling to customers from other GCC countries that have VAT (UAE and KSA at the moment), you need to distinguish between selling to consumers and businesses.
Selling to consumers
If you are selling to consumers (B2C) from another GCC country where there is VAT, you should charge the VAT rate of the country your business is based in.
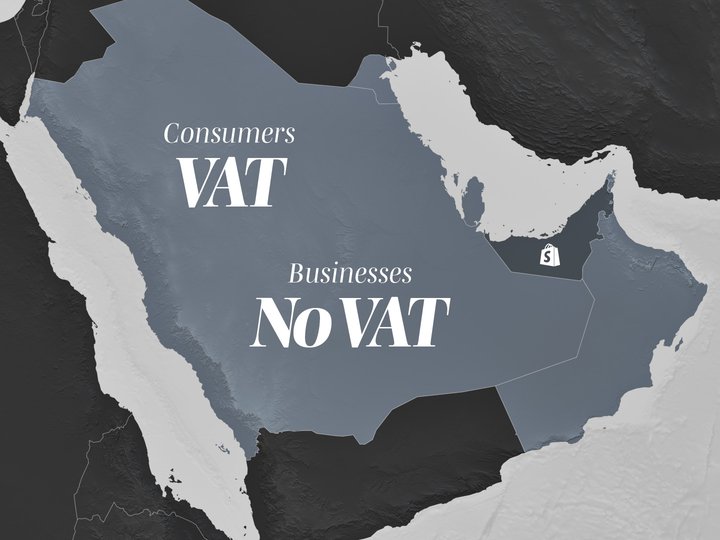
Selling to businesses
If you are selling to VAT registered businesses that are based in another GCC country, you should not charge them VAT.
You are required to always issue proper invoices to your business customers. The invoices need to display the TRN/TIN number of both your business and that of your business customer and need to clearly demonstrate that no tax has been charged.
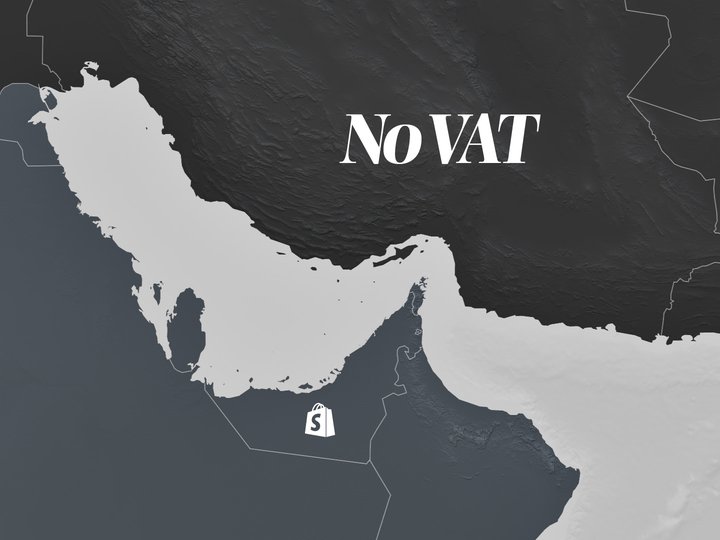
When you are selling to customers outside of the GCC, you should not charge VAT on any goods or services.
You will still need to report the sales for VAT and taxation purposes, but show them as sales with 0% VAT. Valid invoices, such as those created by Sufio, can serve as documentation that the goods were shipped outside of the GCC.
Professional invoices for Shopify stores
Let Sufio automatically create and send beautiful invoices for every order in your store.
Install Sufio - Automatic Invoices from the Shopify App Store
